Unit 4: Work & Energy
Practice Problems

Note: problem difficulty is ranked using a star system.
(*) One-star problems are fundamental to the unit, and can be done relatively quickly. Use these problems to introduce yourself to the material.
(**) Two-star problems are more difficult, and require an understanding of one or two key concepts. Use these problems to test your understanding of the material.
(***) Three-star problems are the most difficult, and require some creative thinking in addition to a deep familiarity with multiple key concepts. Use these problems to challenge yourself; if you can complete one of these, you’re on your way to mastering the material.
*Q4.1) You drop a ball from rest off of a cliff. Ignoring air resistance, find the velocity of the ball as it hits the ground 20m below. Use conservation of energy, and compare your answer to what you would get using kinematics.
**Q4.2) You toss an egg with an initial velocity of 18m/s at an angle of 40 degrees above horizontal in an attempt to hit your friend who’s standing at the bottom of a 25m cliff. Use energy methods to find the speed of the egg as it strikes your friend.
**Q4.3) After deadlifting a 120kg barbell to a height of 1m, you shimmy sideways along the floor a distance of 50cm in a feeble attempt at showboating. You then proceed to drop the weight, causing the barbell to loudly slam into the floor, setting off the Planet Fitness alarms.
a) Find the work done by gravity as you lift the barbell to its maximum height.
b) Find the work done by gravity as you shimmy horizontally while holding the weight at its maximum height.
b) Find the work done by gravity as the barbell falls to the floor.
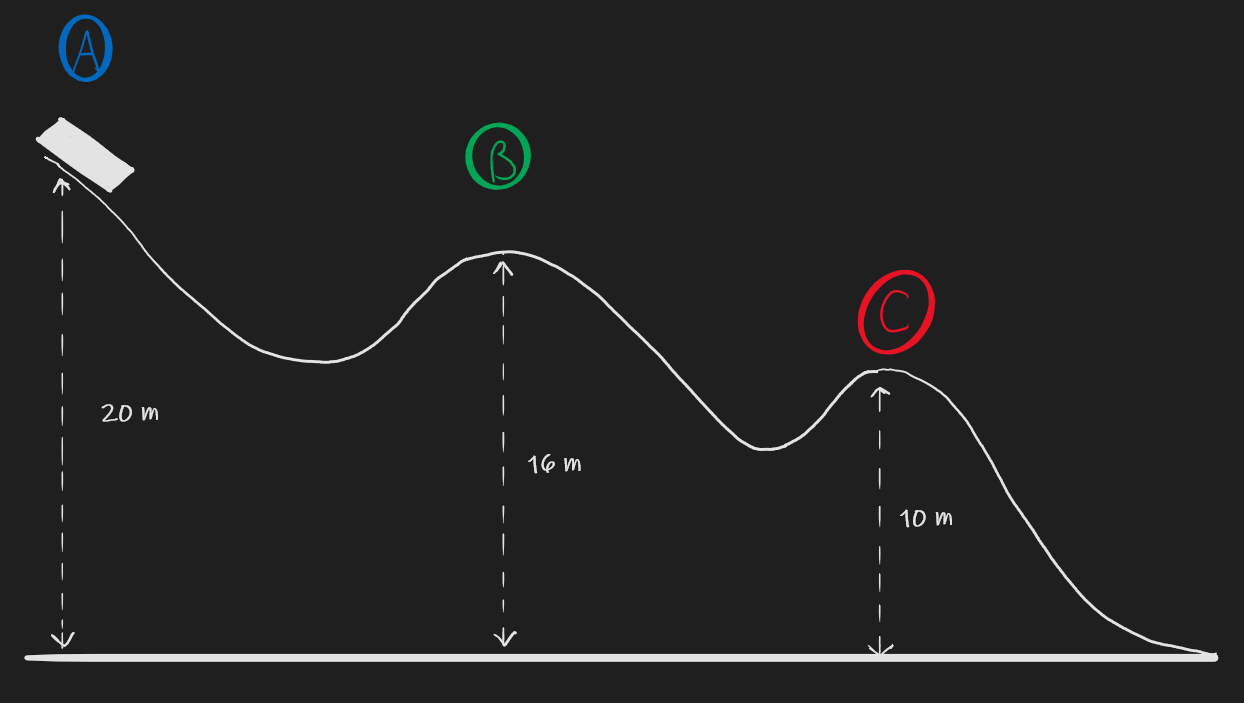
**Q4.4) A block of ice of mass 1kg is released from rest at point A on the ramp shown below. Ignore friction.
a) Find the speed of the block at point B.
b) Find the speed of the block at point C.
c) How much work is done on the block by gravity as the block moves from point A to point C?
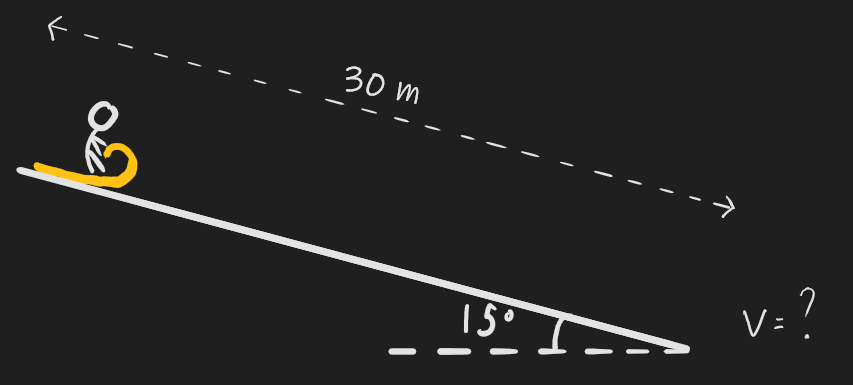
**Q4.5) Initially at rest, you toboggan down a hill inclined at an angle of 15 degrees, reaching the bottom of the hill after travelling 30m along its surface. Given that you release 320 J of thermal energy due to friction as you slide down the hill, find your speed at the bottom. Your mass is 70kg and the mass of the toboggan is 20kg.
**Q4.6) How much food energy is required for you to do 100 pull-ups? Assume that your body mass is 80kg and that your centre-of-mass rises 70cm over the course of a single pull-up. Also assume that your body is 20% efficient at converting food energy into useful mechanical work. Give your answer in Joules and in Calories (remember that 1 Cal = 1kcal = 4184 J).
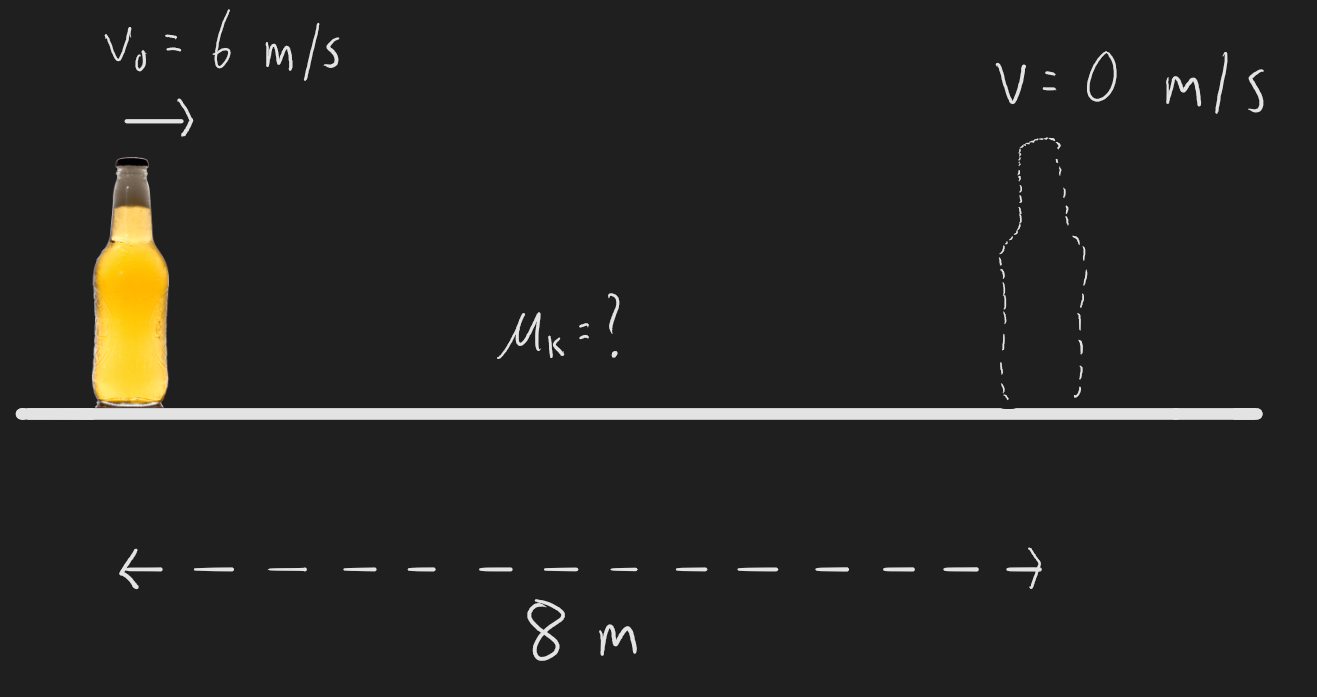
**Q4.7) You pass a bottle of beer to your friend by sliding it along the surface of a bar. Find the coefficient of kinetic friction between the bottle and the bar given that you gave the bottle an initial speed of 6m/s and it came to rest 8m down the length of the bar. Use work/energy methods and compare your answer to what you would find using forces/kinematics.
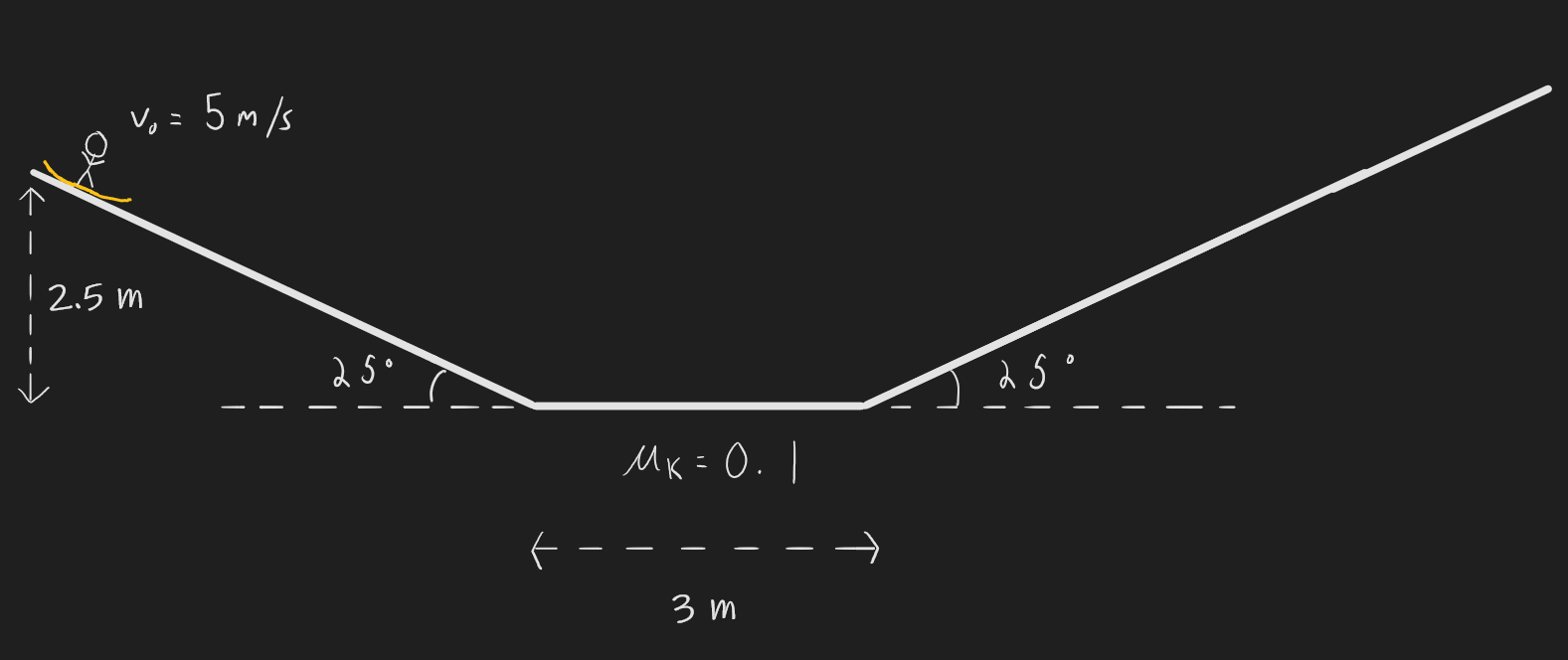
***Q4.8) A snowboarder hits the ramp shown below with an initial speed of 5m/s. Given that the coefficient of friction between her board and the snow is 0.1, find the maximum vertical height that she reaches up the ramp opposite to where she started.