Unit 3: Forces & Newton’s Laws
Practice Problems

Note: problem difficulty is ranked using a star system.
(*) One-star problems are fundamental to the unit, and can be done relatively quickly. Use these problems to introduce yourself to the material.
(**) Two-star problems are more difficult, and require an understanding of one or two key concepts. Use these problems to test your understanding of the material.
(***) Three-star problems are the most difficult, and require some creative thinking in addition to a deep familiarity with multiple key concepts. Use these problems to challenge yourself; if you can complete one of these, you’re on your way to mastering the material.
*Q3.1) You push a box of mass 20kg along the floor, causing it to accelerate from rest to a speed of 4m/s in 6 seconds. You then continue to push the box along the floor at a constant velocity of 4m/s for an additional 10 seconds.
a) What’s the net force on the box for the first 6 seconds?
b) What’s the net force on the box for the final 10 seconds?
*Q3.2) Miley Cyrus (mass 60kg) sits perched atop a wrecking ball of mass 200kg, supported by a cable attached to the ceiling. Find the tension in the cable.
**Q3.3) A bullet of mass 30g is fired from a rifle and accelerated from rest to its muzzle velocity of 300m/s in 0.5ms.
a) What’s the net force on the bullet during the 0.5ms that it is accelerating?
b) What’s the net force on the rifle during this same time period?
c) If the rifle has a mass of 9kg, what acceleration does the rifle experience?
**Q3.4) Your little cousin is throwing a tantrum and grabs a hold of your leg while laying on the floor. Unphased, you continue to walk forward at a constant velocity of 1.5m/s, dragging your cousin behind you with a force of 80N parallel to the floor. Given that your cousin has a mass of 22kg, find the coefficient of kinetic friction between your cousin and the floor.
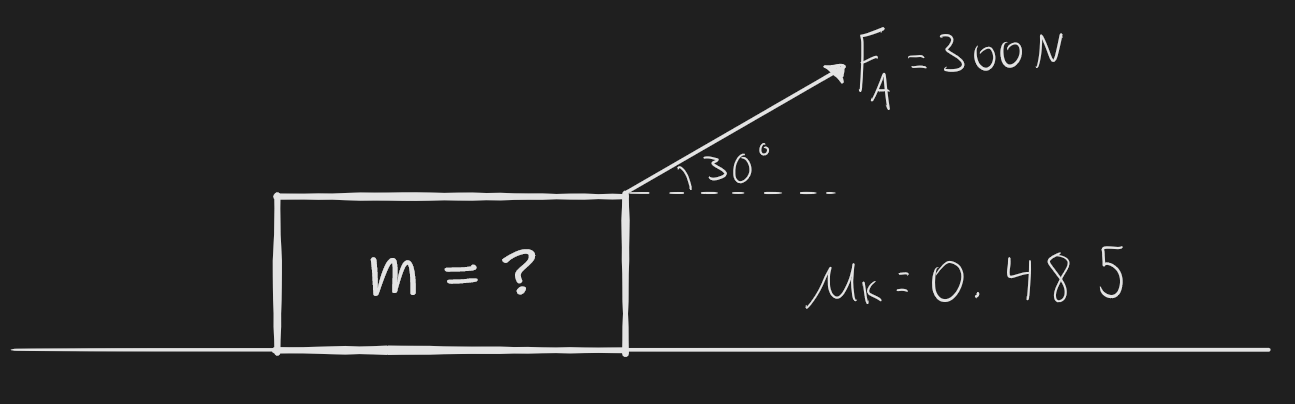
**Q3.5) While spying on your neighbour, you notice him drag a bag of garbage to the curb that is suspiciously human-shaped. You observe that he’s dragging the bag at a constant speed along his horizontal driveway by pulling with a force that you estimate to be 300N at an angle of 30 degrees above horizontal. You later go to your driveway and measure the coefficient of kinetic friction between concrete and a garbage bag to be 0.485. Using this information, estimate the mass of your neighbour’s garbage bag. Could it be a body?
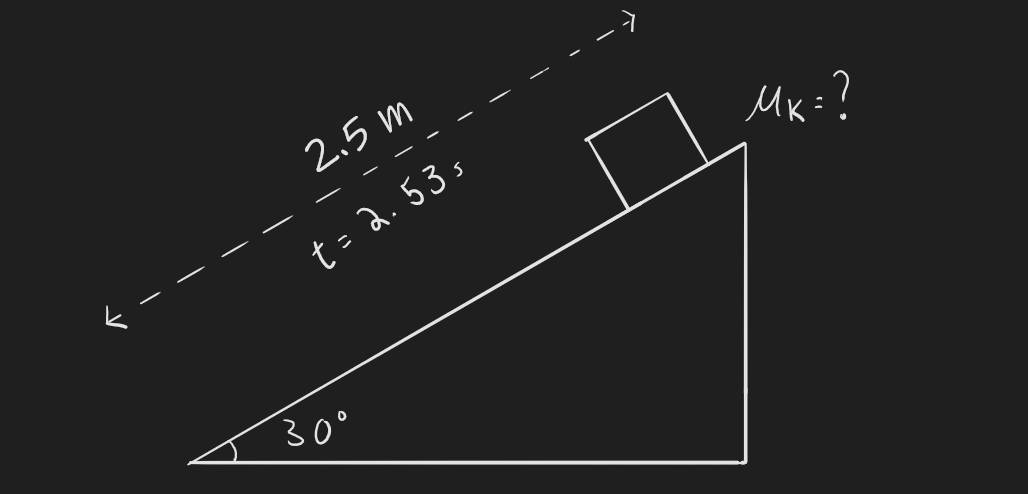
***Q3.6) You found the coefficient of kinetic friction in Q3.5 by measuring the time it took for a bag of your own garbage to slide down the length of your driveway. Using the fact that the driveway is inclined at 30 degrees and that it took 2.53 seconds for the bag to slide down the entire length of the 2.5m-long driveway when released from rest, calculate the coefficient of kinetic friction between the garbage bag and the driveway. Does your answer agree with Q3.5? Hint: the answer does not depend on the mass of the bag.
***Q3.7) WinterLab is a Toronto-based research institute that rates the effectiveness of winter boots by measuring their “MAA” (Maximum Achievable Angle). This is measured by strapping a willing participant into a harness, putting them in a pair of winter boots on a slick icy surface, and increasing the tilt angle of the floor until the participant slips. Calculate the MAA for a pair of boots given that the coefficient of static friction between the boots and the icy floor is 0.2. Hint: the result does not depend on the mass of the participant.
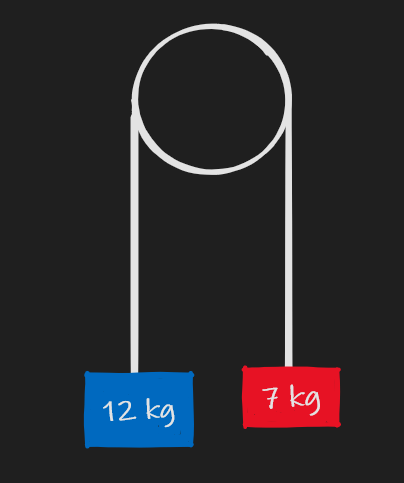
**Q3.8) Two blocks are attached to either end of a cable that is wrapped around a pulley, as shown. Ignoring the mass of the cable, find the acceleration of both blocks.
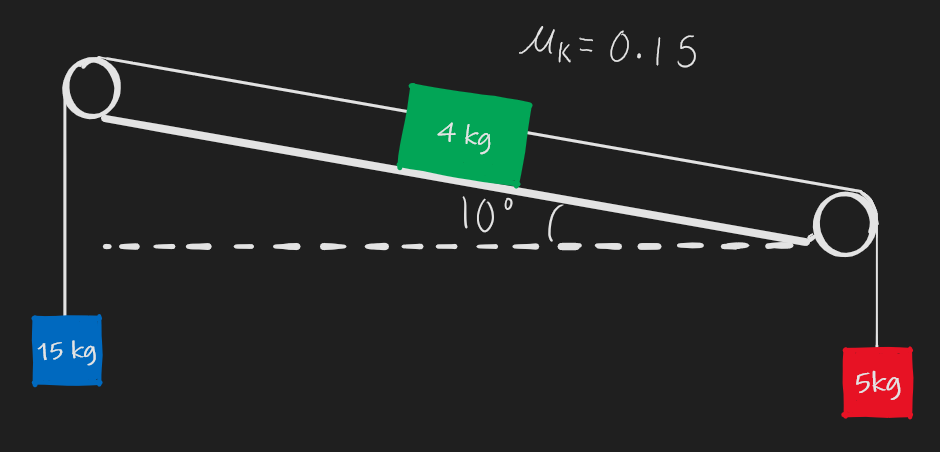
***Q3.9) Three blocks are attached to a cable as shown below. Ignore the mass of the cable.
a) Find the acceleration of the blocks.
b) Find the tension in the cable.
*Q3.10) If you have a mass of 60kg and your crush has a mass of 80kg, with what force is your crush attracted to you if you are separated by 5m?
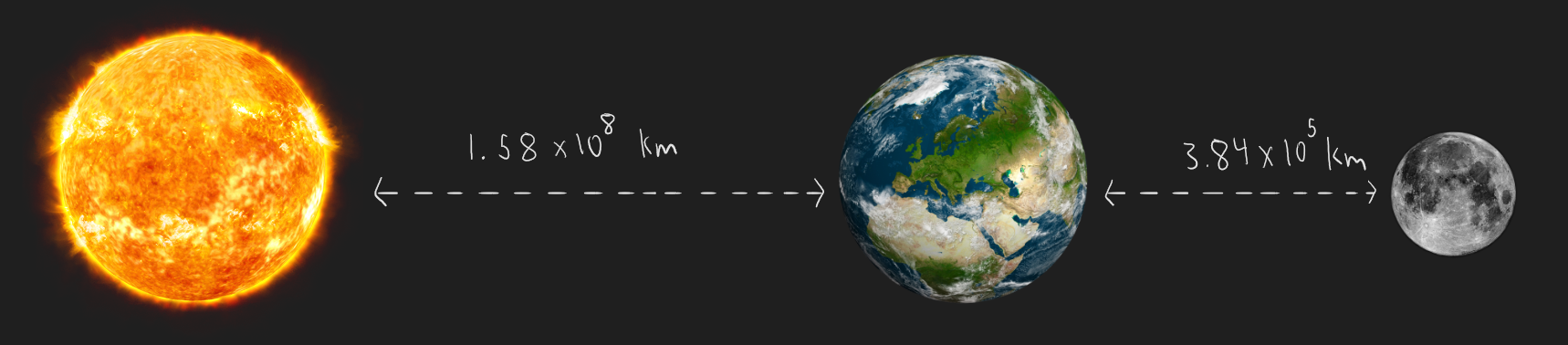
**Q3.11) During a lunar eclipse, the Earth, the Moon, and the Sun are arranged in a line as shown below. What’s the net force on the Earth at this instant? Note: the mass of the Earth, Moon, and Sun are 5.97x10²⁴kg, 7.35x10²²kg, and 1.99x10³⁰kg respectively. The distance between the Earth and the Sun (on average) is 1.58x10⁸km, and the distance between the Earth and the Moon is 3.84x10⁵km.
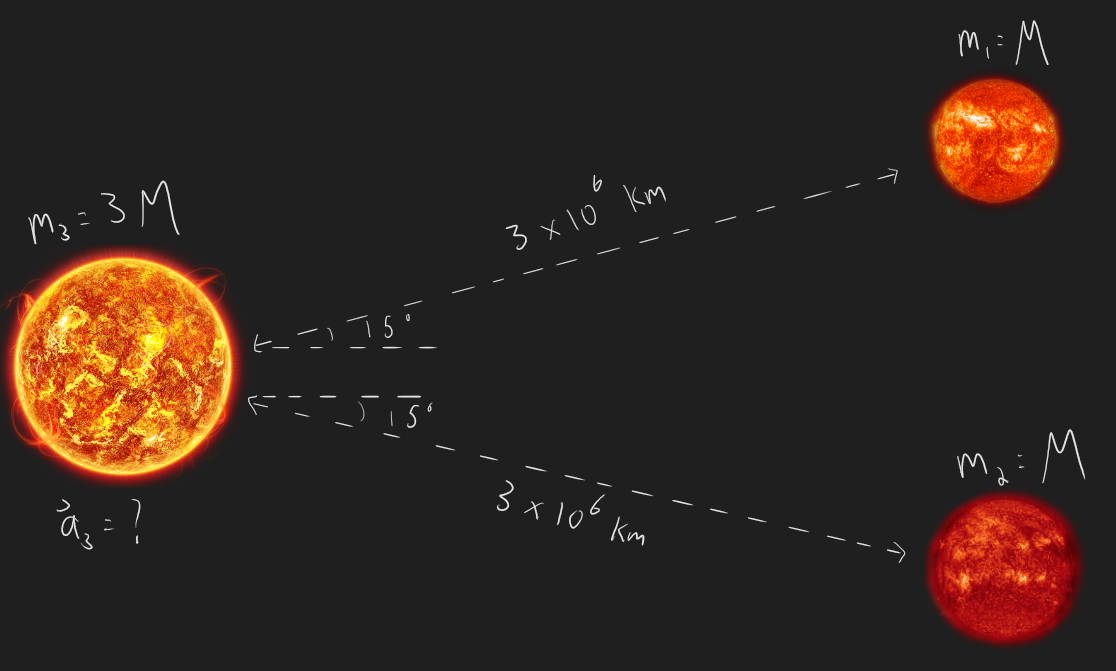
***Q3.12) Some star systems contain two stars orbiting a shared centre-of-mass in close proximity in a so-called binary system. In rare cases, some systems even contain a third star that orbits the centre-of-mass of the binary pair at a greater distance, constituting a so-called ternary system. What’s the acceleration of the third star in the following ternary system at the instant shown below? Note: M = 3.0x10³⁰kg.